Technical Reports: Access to data & tools*
|
SERA work package |
WP 18 / VA 1 |
|
Authors |
M. Landès, R. Steed, R. Bossu |
|
Keywords |
Macroseismology, felt report, felt intensity, web service |
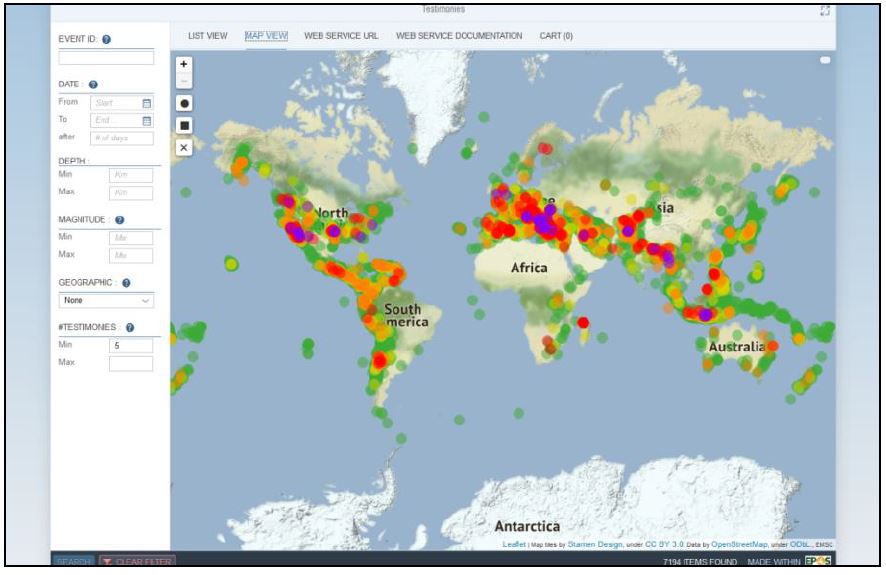
Figure 1. Map view of the felt report service. The left panel allow users to select felt events in time, in space, with magnitudes and by number of collected reports. The map facilitates spatial searches and plots the filtered events.
Main Results
Within the SERA project, the EMSC has developed and maintained a service that provides access to the eyewitness data collected in real time by EMSC. People who feel an earthquake and want to share their experiencehave the opportunity to evaluate the level of shaking via EMSC’s services by selecting from a collection of thumbnail images (felt reports). Bossu et al. 2016 gives a complete description of this collection system. This approach using cartoons replaces the more traditional online questionnaire on our mobile application LastQuakeand on our mobile website (e.g. Bossu, et al., 2015). It is based on 12 thumbnail-sized images conceptualized by a professional cartoonist that aim to depict each level of the EMS-98 macroseismic scale in a culturally neutral way. These thumbnails are available to anyone who wants to integrate them in their collection system offering the chance to homogenizedata collection amongst institutes. In addition to the felt intensity, each felt report has an individual geographical locationeither provided by themobile device when the user has allowed it to be shared or estimated from a postal address given by the user.
Felt reports are collected in real time and associated to seismic events received by the EMSC. Moreover, due to the popularity of the EMSC, felt reports are collected from all continents and, generally, almost 50 % of felt reports are collected only 10 minutes after the earthquake occurrence.This service provides access to felt report data via a graphical user interface or via a web service (useful for scripting access). However, real time data is not available currently due to quality assurance concerns and a dedicated real-time service is under development for registered users.The popularity of felt report data is increasing and beginning to interest the scientific community. Several ongoing studies are trying to incorporate felt intensities in the construction of shakemaps and to constraint rupture models. This service is a valuable resource for such endeavours.
List of Publications
- Bossu, R., Steed, R., Mazet-Roux, G., Roussel, F., Etivant, C., Frobert, L., Godey, S. The key role of eyewitnesses in rapid impact assessment of global earthquakes. (2015) Springer Natural Hazards, S. D’Amico (ed.) Earthquakes and Their Impact of Society 601-617
- Thumbnail‐Based Questionnaires for the Rapid and Efficient Collection of Macroseismic Data from Global Earthquakes, Rémy Bossu, Matthieu Landès, Fréderic Roussel, Robert Steed, Gilles Mazet-Roux, Stacey S.Martin, and Susan Hough. Seismological Research Letter. Oct 2016. doi: 10.1785/0220160120
Access to Data and Services
All EMSC web services are available on the Seismic Portal via the “Web services” link: (https://www.seismicportal.eu/webservices.html). You can also access the felt report service directly at https://www.seismicportal.eu/testimonies-ws/. Some documentation and tutorials can be found on the EMSC github at https://github.com/EMSC-CSEM/webservices101.
|
SERA work package |
WP 19 / VA 2 |
|
Authors |
J. Bienkowski, R. Sleeman |
|
Keywords |
Seismic waveforms, EIDA, ORFEUS, infrastructure |
Federated infrastructure services for seismic waveform data in Europe
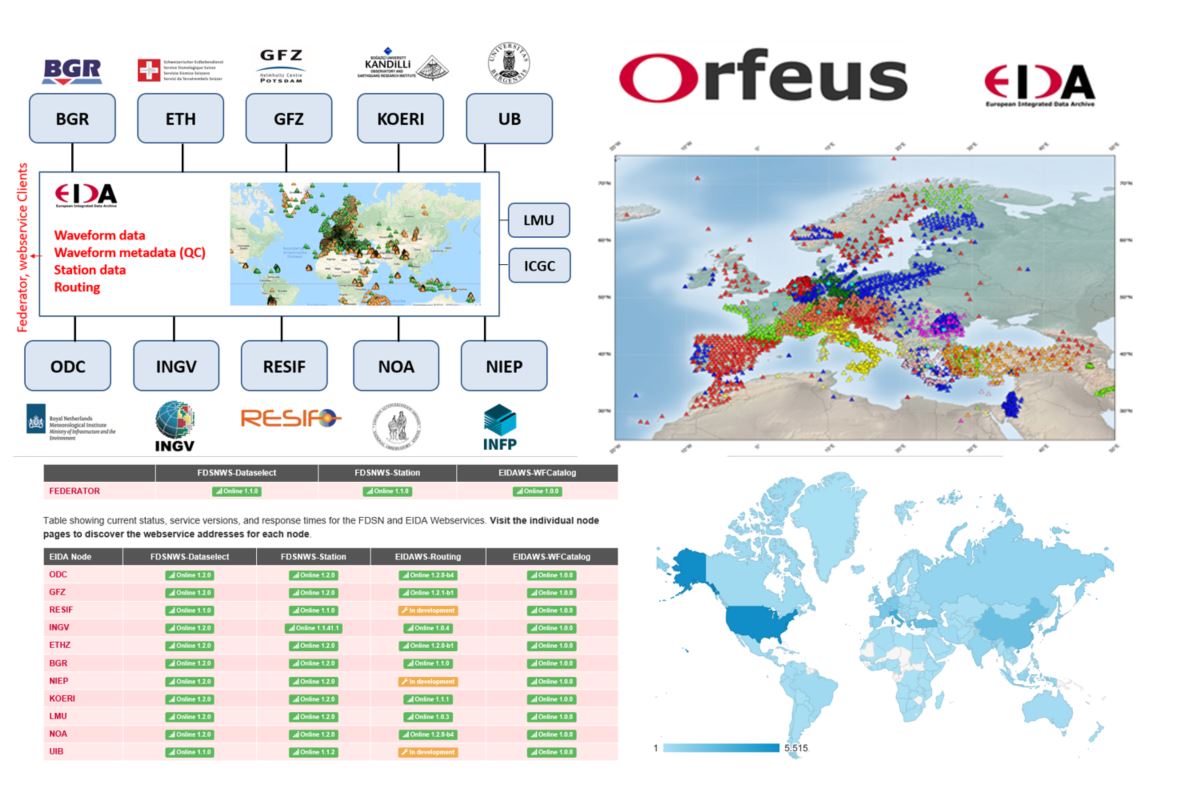
Figure 1. Overview of service provisioning through VA2. Top-left: Federation of European Data Archives (EIDA) providing transparent, standardized access to seismological waveform data collected and curated by (currently) 12 large European archives; Top-right: snapshot of seismic stations in Europe accessible through EIDA; Bottom-left: access to and status of all web services in EIDA, including the recently launched Federator; Bottom-right: global impact of services provided by VA2 for ORFEUS EIDA.
Main Results
The ORFEUS infrastructure is one of the biggest infrastructures in the world that provides seismological data. Furthermore, it derives products to the scientific research community in strong collaboration with European seismological observatories. The infrastructure is organized as a networked system of observatory infrastructures, waveform data archives and services. A key component is the federated, distributed European Integrated waveform Data Archive (EIDA) that transparently connects a number of large data centers in Europe, including the ORFEUS Data Center.
This unique, federated archive serves seismological waveform data from permanent and temporary networks of broad-band sensors and strong motion sensors deployed in Europe and beyond through dedicated, standardized webservices. Currently, EIDA holds beyond 400 TB of data of 107 permanent networks and 190 temporary networks, with more than 11’000 seismic stations in total. ORFEUS EIDA is technically compatible with the EPOS infrastructure and therefore ready to accommodate other types of data to serve a broader solid Earth user community (e.g. earthquake engineering).
The following services are offered to the (seismological) research community to provide (virtual) access to raw waveform data and related metadata:
- ORFEUS website
- interactive EIDA data portal (GUI)
- EIDA standardized webservices
- RRSM (Rapid Raw Strong Motion database)
- StationBook
|
SERA work package |
WP 20 / VA 3 |
|
Authors |
L. Luzi, M. Locati, R. Basili |
|
Keywords |
Open-access data, infrastructures, European Strong Motion Database, European Archive of Historical Earthquake Data, European Database of Seismogenic Faults |
An easier way to get hold of strong-motion records, macroseismic data and seismogenic fault data
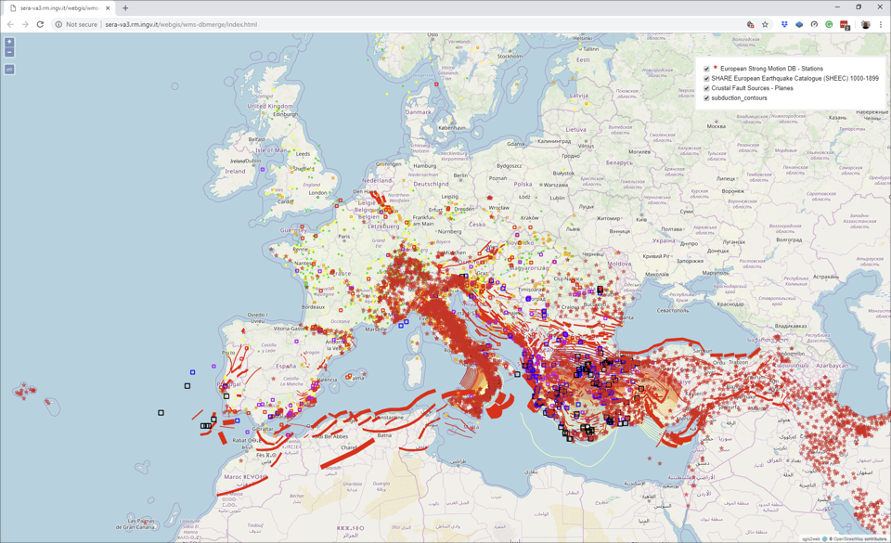
Figure 1. Map view of data provisioning through VA3: recording stations (ESM), historical earthquakes (AHEAD), and seismogenic sources (EDSF).
Main Results
A fundamental task for engineering seismologists is to access the information behind seismic hazard and risk models. In the past decades, the amount of open-access data has dramatically increased due to the advances in information technology and in the development of infrastructures to host data and promote their interoperability. As consequence, there is a significant improvement of dedicated thematic repositories and of tools that facilitate the user to access data and services.
SERA-VA3 aims to bring the data at the users’ fingertips. It offers access to reliable and extensive data sets and services for the community of engineering seismologist as well as other specialists. They include the European Strong Motion Database (ESM), the European Archive of Historical Earthquake Data (AHEAD), and the European Database of Seismogenic Faults (EDSF).
A web portal works as a unified access point to data and services. This portal not only guides the visitors to the three original database portals, but it is also meant to provide an enhanced navigation through the data. The three services are technically compatible with the EPOS infrastructure and therefore ready to accommodate other types of data to serve a wider solid Earth user community, for example earthquake engineering.
|
SERA work package |
WP 21 / VA 4 |
|
Author |
L. Danciu |
|
Keywords |
Earthquake hazard, earthquake risk, seismic hazard, seismic risk, European Seismic Hazard Model (ESHM20), European Seismic Risk Model (ESRM20), web-platform, European Facilities of Earthquake Hazard and Risk (EFEHR) |
The web platform of European Facilities for Earthquake Hazard and Risk (www.efehr.org)
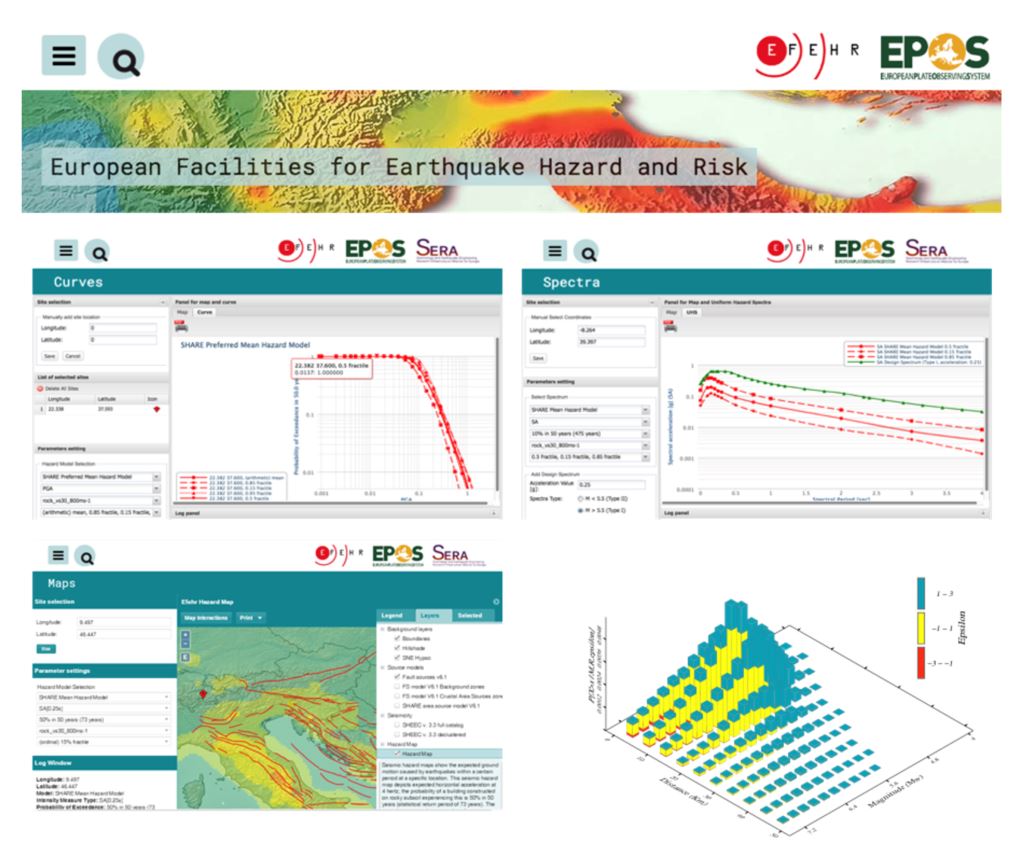
Figure 1. EFEHR web-portal: main web-interfaces to access the hazard curves (top left), uniform hazard spectra (top right), hazard maps (bottom left) and hazard disaggregation (bottom right)
Main Results
The web platform of European Facilities of Eartqhauke Hazard and Risk (EFEHR) provides access to specialized datasets, input models, results, documentation and information. Within SERA VA4 activities, the web-platform has been further developed and upgraded, from web-content to web-viewers (i.e. hazard curves, maps and uniform hazard spectra). The web-services metadata has been upgraded to meet the EPOS-ICS requirements ensuring access in a fully discoverable, searching metadata environment of the EPOS main services. Model Development Tools (MDTs) and components for building and running the hazard models with OpenQuake are also provided. The web-traffic analytics of the EFEHR web-portal indicates a preference for users to access the hazard maps and uniform hazard spectra. The visitors are distributed worldwide. Oftenly, the visitors are consulting the hazard values at a specific site, rather than downloading entire sets of results and/or models. The hazard map viewer is the most used web application. Especially, after a destructive earthquake in the Euro-Mediterranean region occured, e.g. the 2019 M6.4 earthquake in Albania, the traffic of the web application increases shortly after the occurrence of an earthquake. The EFEHR data and models are collected and stored from completed scientific projects for long-term archiving, documentation, accessibility and use in research, support decision making and mitigation actions.
Access to Data and Services
EFEHR web-portal provides a single access point for data, models and results. No user authorization is required. Currently, the EFEHR web-portal provides open access to the following models:
- The 2020 European Hazard and Risk Model developed within the SERA JRA3 and JRA4
- The 2013 European Seismic Hazard Model (ESHM13, Woessner et al 2015)
- The 2014 Earthquake Model of the Middle East (EMME14, Giardini 2018)
- The 2015 Swiss Hazard Model (SuiHaz15, Wiemer et al 2015)
- The 1999 Global Hazard Map of the Global Seismic Hazard Assessment Program (GSHAP, Giardini 1999)
|
SERA work package |
WP 22 / VA 5 |
|
Authors |
M. Sobiesiak, P. Sałek, S. Lasocki |
|
Keywords |
Induced seismicity, anthropogenic hazards, comprehensive datasets on anthropogenic seismicity, EPOS Thematic Core Service Anthropogenic Hazards, IS-EPOS Platform |
Virtual access to the data and applications of anthropogenic seismicity and related hazards
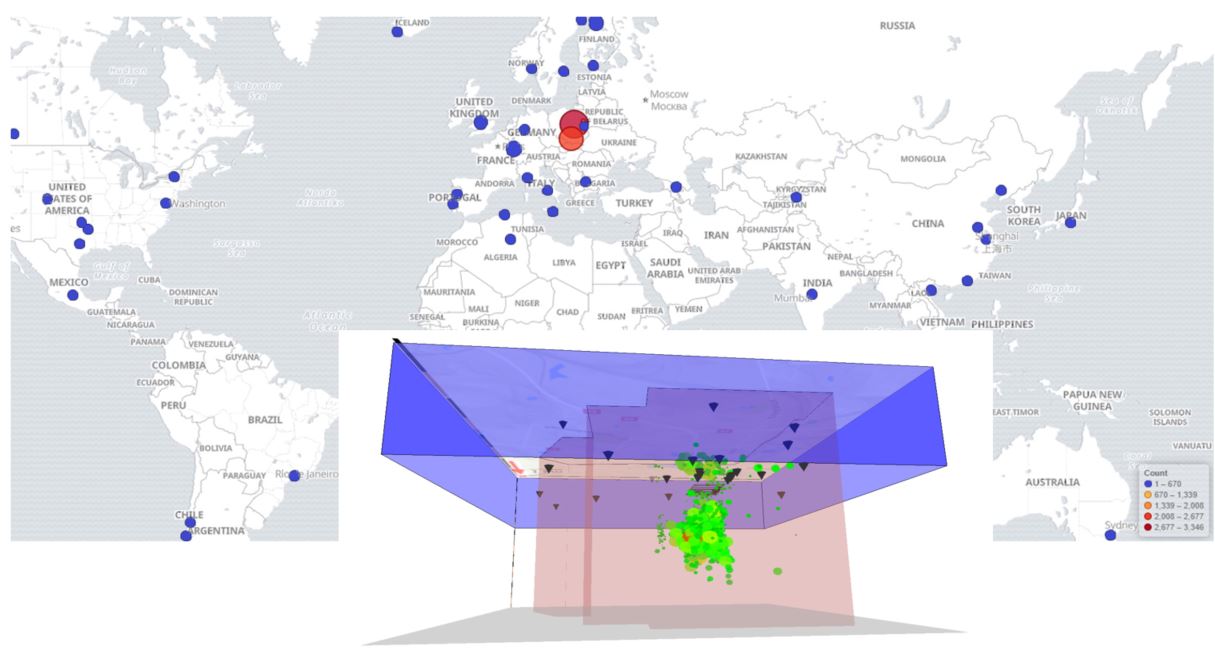
Figure 1. Background: map of global user logins. This map demonstrates the global usage of the IS-EPOS platform that integrates research infrastructure of EPOS TCS AH. Foreground: example of what is possible to do with the platform. Figure shows a 3D sketch of induced seismicity distribution in Bobrek Coal Mine, Poland.
Main Results
Within the framework of Virtual Access (VA5) of WP22 in the SERA project, we are providing 19 new episodes of anthropogenic hazards. In total, 25 episodes from 10 different countries are openly available. These are up to now nine episodes more than originally planned. An episode of anthropogenic seismicity contains seismological catalogues, event based or continuous waveforms of seismic signals, technological data on seismicity inducing industrial activities, geological and tectonic settings, and information on environment. This facilitates research aiming at understanding the interactions between the parameters of the industrial activities and the anthropogenic seismicity. The virtual access gives researchers and other interested or concerned groups in society a chance to gain information on detailed knowledge. The number of registered users of IS-EPOS platform is 1094.
Access to Data and Services
Access to the website of IS-EPOS platform is through https://tcs.ah-epos.eu/
List of episodes, available for SERA members and the general public:
|
Name of episode |
Type |
Location |
|
Asfordby |
underground mining |
GB |
|
Bobrek Mine |
underground coal mining |
PL |
|
Czorsztyn |
shallow water reservoir |
PL |
|
Cotton Valley |
hydrocarbon extraction |
USA |
|
Gazli |
hydrocarbon field |
UZ |
|
Gisos-Cerville |
underground solution mining |
FR |
|
Groningen Field |
hydrocarbon production |
NL |
|
Gross Schoenebeck |
geothermal energy experiment |
GE |
|
Lacq Gas Field |
conv. Hydrocarbon extraction |
FR |
|
LGCD |
underground copper mine |
PL |
|
Lubocino |
shale gas |
PL |
|
Monteynard |
water reservoir |
FR |
|
Northwich |
salt extraction cavities |
GB |
|
Oklahoma |
hydrocarbon extraction |
USA |
|
Preesall Mine |
salt extraction cavities |
GB |
|
Preese Hall |
shale gas |
GB |
|
Pyhasalmi Mine |
hydrocarbon extraction |
SU |
|
Song Tranh |
deep water reservoir |
VIE |
|
Starfish |
underground gas storage |
FR |
|
The Geysers |
geothermal field |
USA |
|
The Geysers Prati 9 and Prati 29 cluster |
geothermal field, enhanced catalogue |
USA |
|
Thoresby Colliery |
underground coal mine |
GB |
|
USCB |
underground coal mining |
PL |
|
Vouglans |
water reservoir |
FR |
|
Wysin |
shale gas |
PL |
For further details please contact Mr. Piotr Sałek: psalek@igf.edu.pl
Downloads*
D2.17 Final compilation of technical reports
*This version of the technical reports has to be accepted by the European Commission.